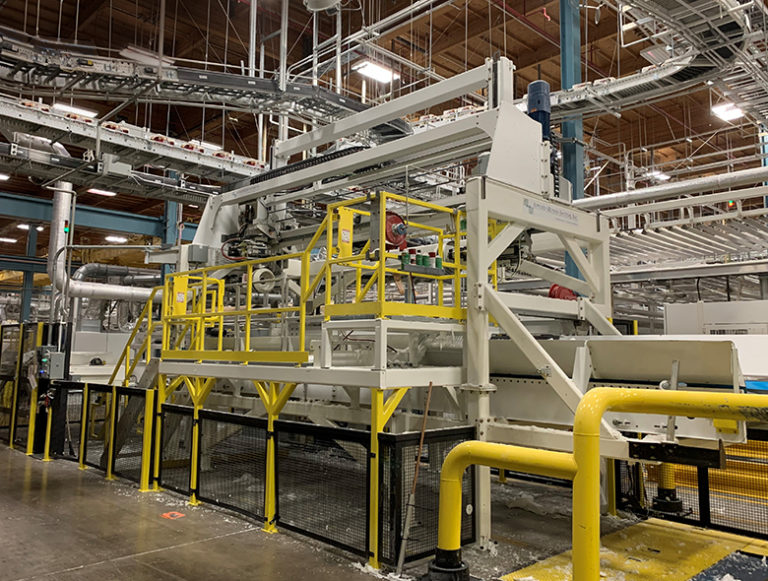
This first-generation solution is capable of cleaning 32-inch diameter spent rolls at a rate of 20 rolls per hour. With its compact construction, it can clean spent rolls up to 48 inches in diameter while fitting under overhead conveyors at an elevation of 15 feet. This machine efficiently cleans rolls from all tissue converting lines in this converting complex and completely eliminates manual labor, risk of injury, and core damage associated with this task.
Safe, sustainable paper core cleaning
Our engineers spend significant time in paper plants across North America and one arduous task that no plant personnel seems to like is the manual process whereby paper is cleaned from the cores of spent parent rolls pulled from the converting lines.
Our team took up the challenge to develop and deploy a core cleaner capable of safely removing all paper from spent parent rolls while significantly extending the life of parent roll cores. Today, we offer this core cleaner as an OEM solution, along with an alternate design that offers significant advantages to paper converters who use a wide range of core diameters and widths.
Safety challenges in paper converting
Prior to deployment of this core cleaner, plant personnel were responsible for slabbing remaining paper from the spent parent roll core to prepare it for reuse back at the paper machine. This process often involved the use of sharp cutting blades and dealing with heavy blankets of broke. Despite protective gloves and safe work practices, operators often risked lacerations and repetitive motion injuries. Also, after many cycles of this manual approach, the outer layers of the core suffered accumulated cutting damage that could lead to failure during the next turn-up operation and as such were discarded after a limited number of uses.
First-generation efforts:
Precisely automated cleaning
This core cleaner was fitted with distance measuring sensors that scan the spent parent roll as it enters the machine on a conveyor giving the system precise awareness of roll diameter and location. The lifting carriage then moves to grip the core internally with inflatable chucks and lifts the roll to engage a linear carriage-mounted saw, which traverses the roll to cut away 2-inch thick blankets of paper that fall to the conveyor below. This process automatically repeats until only a ¼ inch of paper is left on the roll. At this point, an oscillating air knife cuts through the final layers without damage to the core. Next, the core spins while a contrast sensor makes one final pass to identify any remaining paper or glued-on remnants. These areas are scrubbed with the air knife, leaving the core clean and ready for reuse at the paper machine.

Second generation:
Flexibility across all roll and core sizes
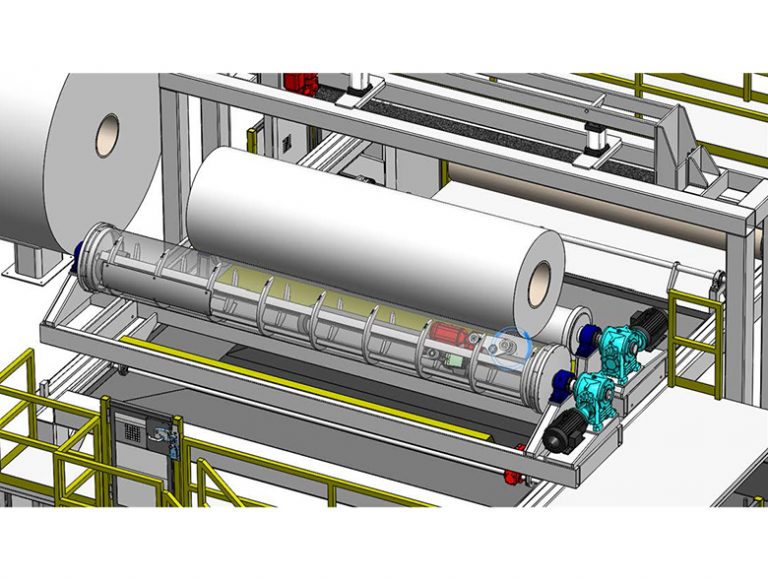
Our first generation core cleaner is a great solution when plants have a consistent core diameter and roll width, however not all plants have this level of uniformity. AMS’s second generation core cleaner is designed to accept paper rolls of any width and any diameter, wound on any size core. The key to this design is the placement of the cutting blade inside one of the support rolls on which the parent roll is loaded. This feature makes it possible to seamlessly switch between a broad range of roll widths and spent roll diameters with varying core diameters.
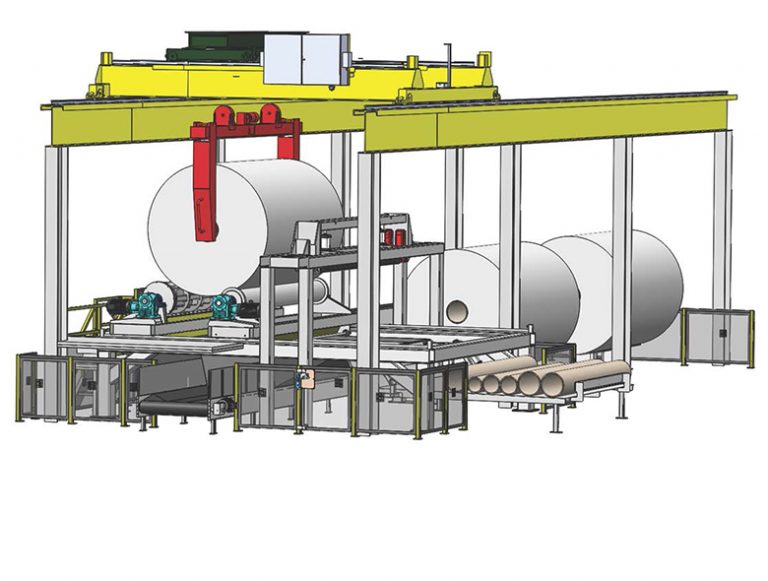
An overhead crane places the spent roll onto a pair of support rolls. The support roll with the integrated sawblade then rotates until the saw blade is aligned with the center of rotation of the spent roll. The blade is then extended and traverses the width of the roll, cutting through layers of paper. After completing a cut, the saw blade retracts, and the integrated saw/roll rotates one revolution and repeats the cutting process. The paper slabs drop to the conveyor below after each cutting cycle. The pair of support rolls are mounted on moving carriages, which allow them to move closer to one another to optimally support the spent roll as paper is removed and roll diameter decreased. These carriages also serve as transports for the roll as it moves from the infeed station to the slabbing station to final cleaning at the scrubbing station.
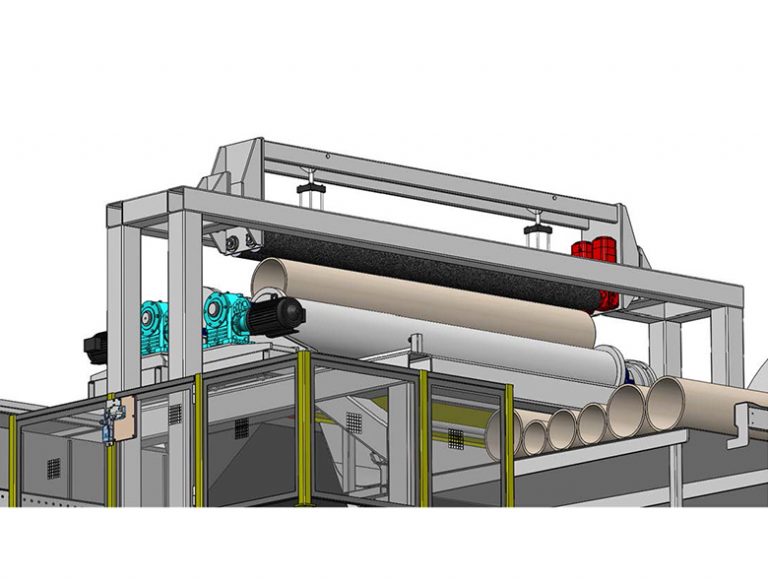
Once the bulk of paper has been removed by the saw, the support rolls carry the core to the final cleaning station. At this stage, the core is centered under the scrubbing rolls, which lower onto the core and counter-rotate to remove the remaining paper and glue as the support rolls slowly spin the core. With the core now fully cleaned, the scrubbing rolls are raised, and the support rolls separate to drop the core onto guides leading to the cleaned core rack.
Reliably safer processes
The AMS core cleaner has operated continuously since deployment in 2017 and enjoyed better than 99 percent up time liberating operators from this strenuous work and eliminating associated injury risk and core damage common to this task. To learn more about how an AMS Core Cleaner solution can improve your converting operations, contact us.
start the conversation
All of our collaborations begin with an open dialogue.
Get in touch with us using this simple form, and a member of our team will follow up with you soon.